Income Effect Meaning And Example

Price also plays a role.
Income effect meaning and example. Income is not the only factor to consider when discussing income effect. The income effect is a phenomenon observed through changes in purchasing power. In microeconomics the income effect is the change in demand for a good or service caused by a change in a consumer s purchasing power resulting from a change in real income. Income effect definition the income effect is the effect on real income when price changes it can be positive or negative.
For example as the price of goods and services increases there will be. This ruled out income effects as an explanation for the endowment effect. For example if a household spends one quarter of its income on rice a 40 decline in rice prices will increase the household s disposable income which they can spend in purchasing either more rice or something else. A part of this increase is due to the real income effect i e.
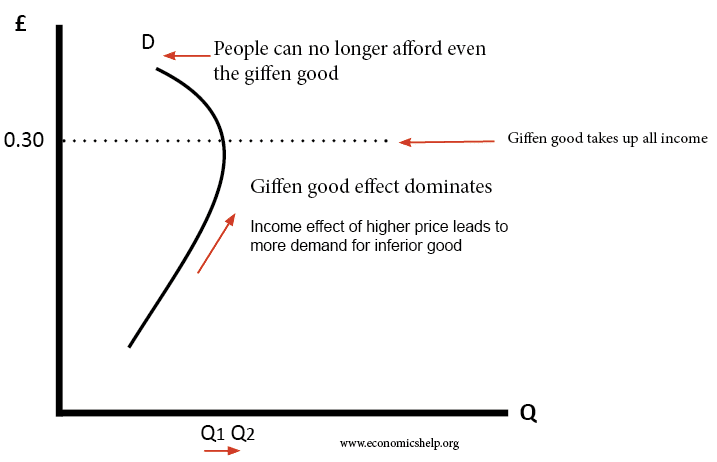
The income effect describes how changes in disposable income caused by wage rises falls changes in tax rates or prices going up or down influence the demand for one product or service or another good or service. In the diagram below as price falls and assuming nominal income is constant the same nominal income can buy more of the good hence demand for this and other goods is likely to rise. It means that as the price increases demand decreases. The effect of changes in things such as prices taxes and costs of services on people s incomes.
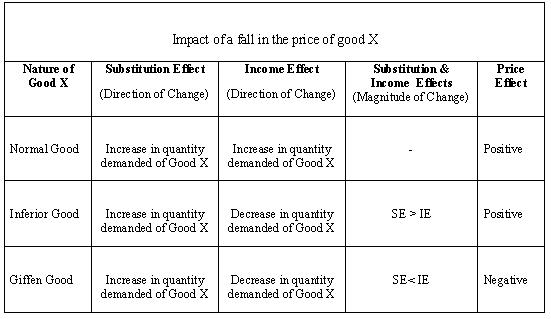
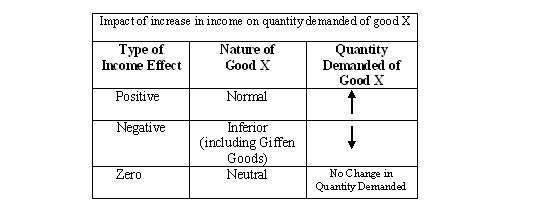
The decrease in quantity demanded due to increase in price of a product. The change in consumers real income resulting from a change in product prices. Utility is broadly considered. Income effect and substitution effect are the components of price effect i e.
It is important to note that we are only concerned with relative income i e income in terms of market prices. The income effect expresses the impact of higher purchasing power on consumption. For a good as a result of a change in the income of a consumer. This explains the negative income effect on consumption.
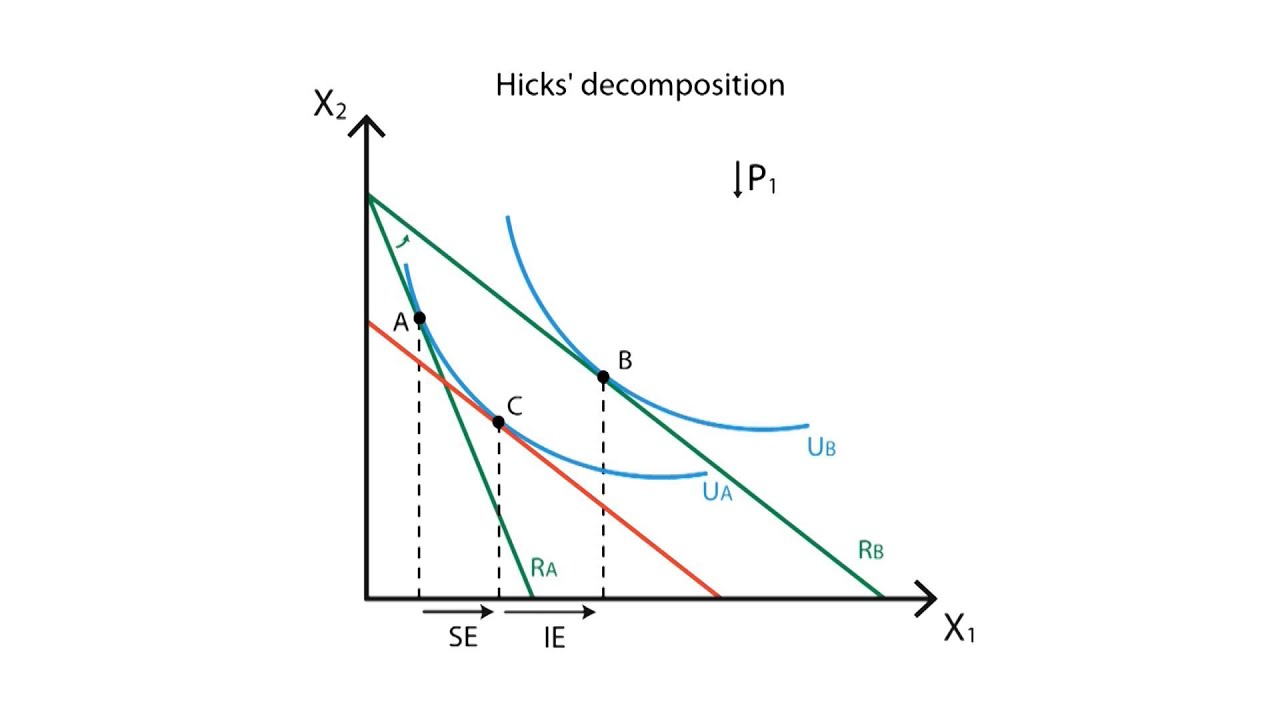
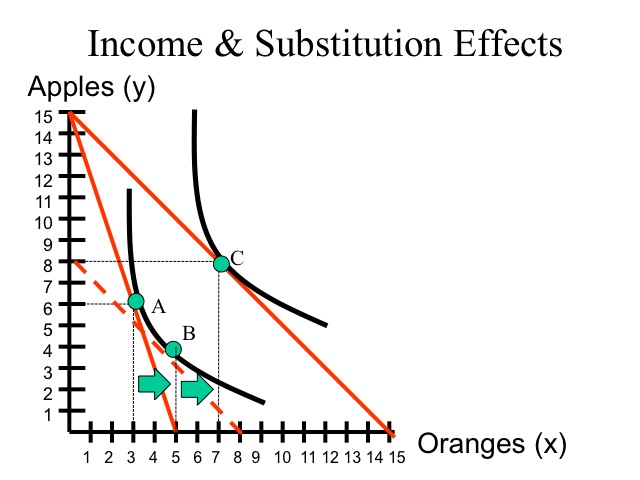
Income effect and price. Thrall introduces a consumption theory of land rent that includes income effects. Income effect arises because a price change changes a consumer s real income and substitution effect occurs when consumers opt for the product s substitutes. The substitution effect describes how consumption is impacted by changing relative income and prices.