Income Gap Definition Economics

So when it comes to economic inequality the problem runs deeper than just differences in our finances.
Income gap definition economics. In many cases of economic inequality wealth flows disproportionately towards a small number of already financially well off individuals. Why inequality keeps rising by the organisation for economic co operation and development oecd sought to explain the causes for this rising inequality by investigating economic inequality in oecd. A 2011 study titled divided we stand. Income inequality is an economic concept that tends to hit some segments of populations harder than others with significant wage gaps often identified for women african americans and hispanics.
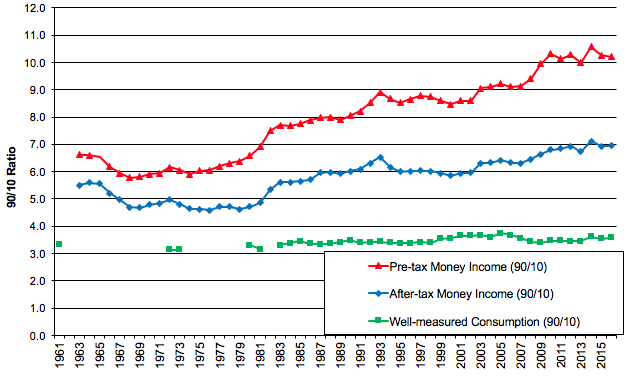
In broad strokes the income gap is the difference between the rich and the poor. Political discourse income inequality is often expressed as the gap between the 1 and the 99. Income inequality or income disparity is the degree to which total income is distributed unevenly throughout a population. It affects and is affected by many other forms of inequality such as.
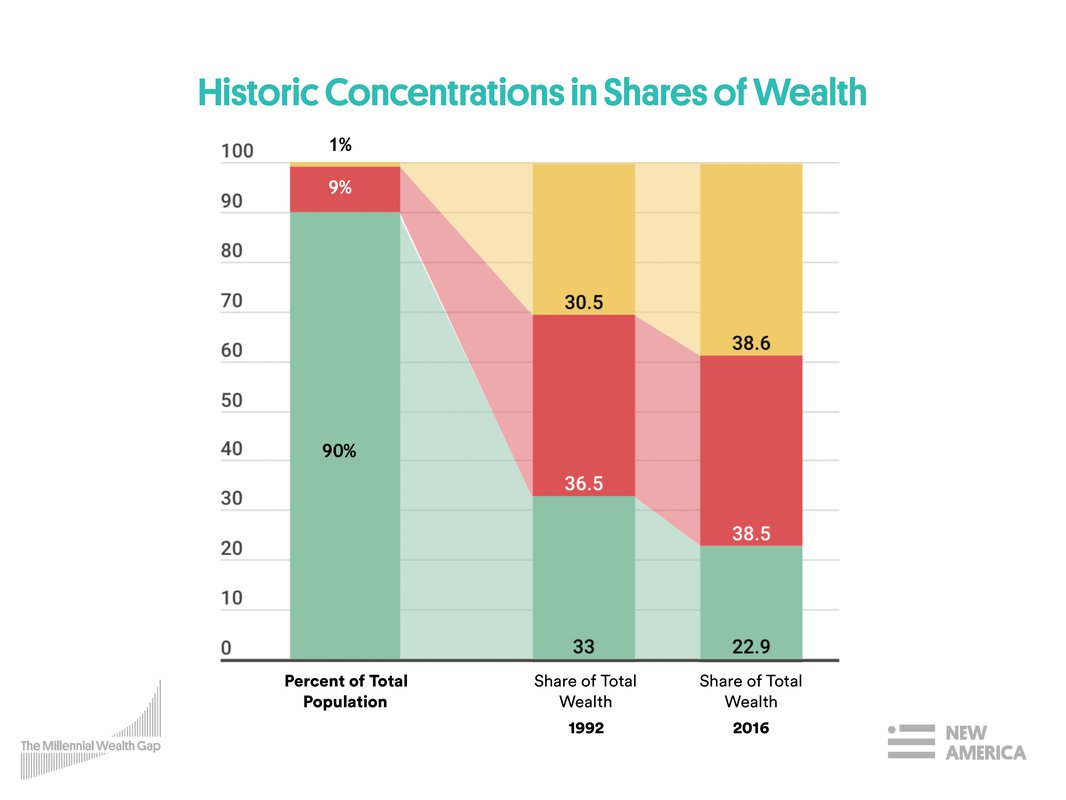
Income inequality in economics significant disparity in the distribution of income between individuals groups populations social classes or countries. A basic definition of economic inequality refers to the disparities in incomes and wealth in a society. In 1820 the ratio between the income of the top and bottom 20 percent of the world s population was three to one. Here s what some of these ideas might be called elsewhere.
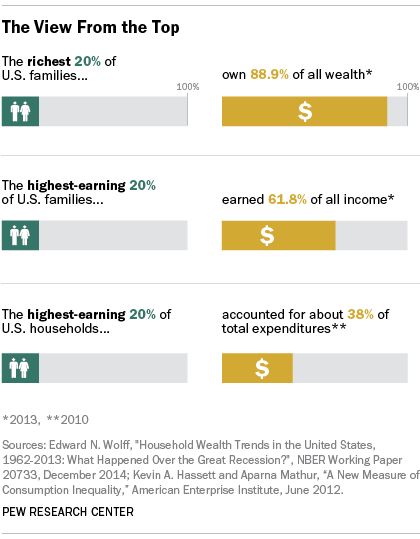
In the united states people with top tier incomes are often called the one percent referencing the fact that they make up a tiny fraction of the overall population while harboring a large percentage of the country. Most americans believe in meritocracy the idea that people advance in wealth and status. Looked at in terms of the whole economy the commonest income gap is that between rich and poor with the rich usually being defined at the top 20 of income earners the top quintile and the poor the bottom 20 bottom quintile. Income inequality is a major dimension of social stratification and social class.
Assets income inequality revenue streams trade off wealth.